Our previous article focused on the benefits of ketones independent of whether induced by diet (e.g., carbohydrate restriction) or exogenous ketones. That article discussed the mechanisms to explain these benefits, whereas the focus of this article is how these benefits apply to real-world situations.
If you haven’t read it already, we recommend checking out our previous blog post on the differences and similarities between ketogenic diets and exogenous ketones. Not only do we discuss the physiological and metabolic differences between the two, but we also make mention of where exogenous ketones may actually offer an advantage over ketogenic diets. There are scenarios when achieving nutritional ketosis via supplementation can be a therapeutic strategy for all of the applications below.
Introduction to Exogenous Ketones
The development of exogenous ketones dates back nearly 50 years, though only within the last decade have they gained more popularity. This resurgence followed the development of different ketone formulations together with research suggesting that ketone bodies themselves are responsible for the many benefits of ketogenic diets. Elevation of blood ketone levels/ ketosis has been found to have several therapeutic and general health applications, whether induced by diet, fasting, or exogenous ketones. These benefits are partly due to the signaling roles of the ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), which has been shown to suppress oxidative stress and inflammation. The first documented performance-enhancing effects of exogenous ketones in elite cyclists further increased interest in these molecules.
What makes exogenous ketones useful in the first place?
Exogenous ketone supplements allow for immediate induction of ketosis without overhauling your diet or making any other changes. Research continues to support the efficacy of exogenous ketones as a practical and reliable way to achieve ketosis, regardless of what you eat.
In a previous article, we discussed the differences between ketogenic diets and exogenous ketones. One of the major advantages of exogenous ketones is that they induce a level of ketosis that is difficult to achieve, let alone maintain, with a ketogenic diet only. Some people are also unable or unwilling to follow a ketogenic diet, even when managing a disorder that benefits greatly from it. Exogenous ketone supplements circumvent the dietary restrictions associated with getting into a state of nutritional ketosis and therefore offer an alternative route. We encourage you to check out the article linked above to learn more about the possible advantages of one over the other, depending on the application, since they are not always interchangeable. The focus of this article is to discuss the potential benefits and applications of exogenous ketone supplements based on current research.
What are some potential benefits of taking exogenous ketones?
Though growing rapidly, the research on exogenous ketone supplements is relatively new, and there are many questions still unanswered. However, the benefits seem wide-reaching and apply not only to where a ketogenic diet may be efficacious, but beyond due to the role of a ketone molecule as both an energy substrate and signaling molecule. Stimulating a state of ketosis with exogenous ketones can turn on genes and have signaling effects that promote a healthier metabolic state over time, affecting health and disease on a whole-body level. Exogenous ketones have been suggested to protect our metabolic health in high-stress environments in part by upregulating our cellular antioxidant potential, protecting cells from oxidative damage, and supporting mitochondrial function. For everyday life, exogenous ketones may help boost energy and mental clarity, manage appetite, lower inflammation, and improve overall metabolic health. Therapeutically, and for these same reasons, exogenous ketones hold a lot of potential for the medical applications below.
Brain Health & Neurological Disorders
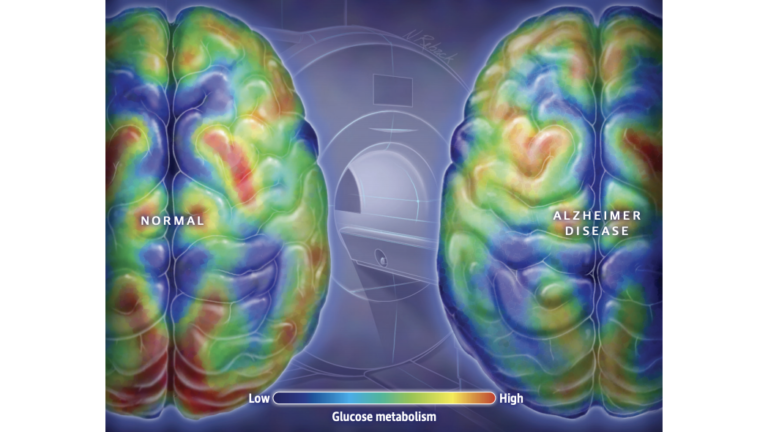
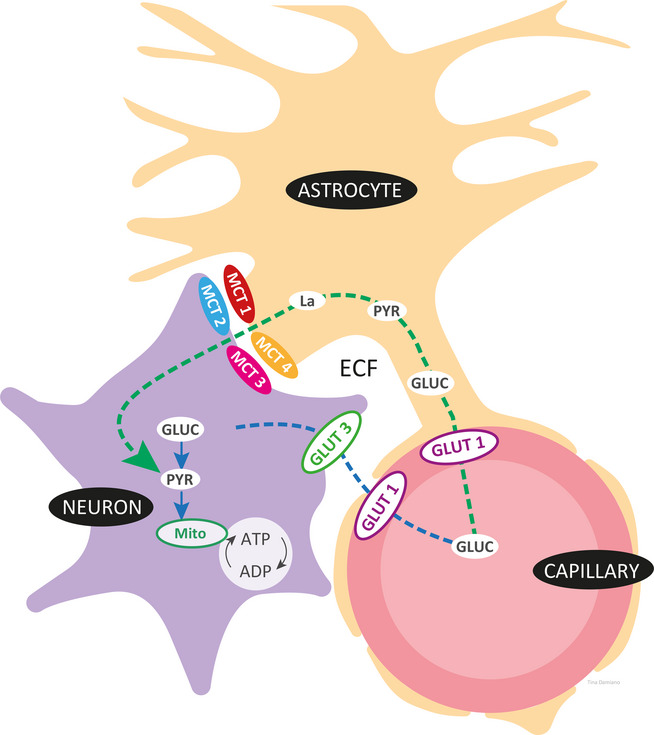
Exogenous ketones as an alternative energy source to glucose are of particular interest for brain health. Unlike glucose, the brain will use ketones in proportion to what is in circulation. Which means that higher blood ketones present more energy for the brain. Since it can be challenging to sustain elevated ketone levels with a ketogenic diet alone, exogenous ketones are useful to deliver immediate fuel to the brain. This can be a practical advantage for anybody, but may be especially therapeutic for those treating disorders associated with impaired brain glucose uptake/utilization, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, glucose transporter type-1 deficiency syndrome (GLUT-1 DS), traumatic brain injury (TBI), strokes, among others. Beyond ketones as a fuel substrate, they also offer neuroprotection through their anti-inflammatory effects, antioxidant potential, mitochondrial support, balancing of the neurotransmitters GABA and glutamate, among other potential mechanisms.
Epilepsy and Seizures
- The ketogenic diet is an established therapy for epilepsy and it is believed that ketone bodies are, at least in part, responsible for the anti-seizure effects of ketogenic diets. Emerging preclinical research suggests that exogenous ketones could be used to complement a ketogenic diet or be a potential alternative to dietary treatments for epilepsy and other seizure disorders. Additionally, seizure control is more likely reached at blood ketone levels that are difficult to achieve with a ketogenic diet alone, suggesting that exogenous ketones may help. Human data is still lacking in epilepsy and seizure disorders, but the preclinical research and anecdotal reports certainly make it an area worth studying. There is currently an ongoing clinical trial evaluating the effects of a nutritional formulation containing exogenous ketones for Angelman syndrome – a genetic disorder characterized by drug-resistant seizures. The results of this trial will help guide the use of exogenous ketones for seizure control.
Neurodegeneration (Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease)
- The neuroprotective effects of ketone bodies have been suggested to prevent, slow, or treat progressive neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Many of the underlying features shared among these disorders, such as mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, and reduced brain glucose metabolism/insulin resistance, intersect with ketone metabolism and signaling. Thus, supplying exogenous ketones represents a reasonable means to target these underlying features. Also, glucose and ketone tracer studies have identified that while brain glucose metabolism may be impaired, ketone metabolism remains intact in the degenerating brain.
- There is plenty of preliminary data to suggest exogenous ketone supplements may represent a potential therapy for neurodegenerative diseases. A 2019 meta-analysis found that medium chain triglycerides (MCT) – a ketogenic fat that elevates blood ketone levels independent of diet – improves cognitive outcomes in Alzheimer’s patients. Also, a recent RCT found that 6-months of MCT supplementation improved cognitive function in patients with mild cognitive impairment, a state that typically precedes Alzheimer’s disease. Compared to MCTs, exogenous ketones may elevate blood ketones to an even greater degree and may be even more beneficial since outcomes have been found to correlate with blood ketone levels. There is an active clinical trial assessing the effects of exogenous ketones in patients with Parkinson’s disease based on previous research showing exogenous ketones to improve mitochondrial function and enhance motor function since mitochondrial dysfunction is a major feature of the disease. We anticipate that more studies will investigate the use of exogenous ketones in these disorders and look forward to future research, as more human data is needed.
Brain Injury
- Traumatic brain injuries (TBI) and other forms of brain injuries are often accompanied by an energy crisis (impaired brain glucose metabolism) further aggravated by increased oxidative stress and neuroinflammation – all of which are targets of ketosis. An imbalance in favor of the excitatory neurotransmitter, glutamate, is also typical following brain injury, and ketones have been found to enhance the conversion of glutamate to GABA, thereby protecting against glutamate excitotoxicity. Interestingly, studies have found that ketone body transporters and enzymes may increase following brain injuries, therefore favouring ketone metabolism. It is possible that the immediate administration of exogenous ketones following brain injury may rescue and/or prevent further brain damage since ketone bodies would bypass impaired glucose metabolism and help to restore and preserve brain energy metabolism. This has been shown in an animal model of TBI where intravenous beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) saved the brain from an energy deficit post-injury. In addition, a ketogenic diet has been proposed to protect the brain during/after a stroke, and there is evidence from animal models showing exogenous ketones to improve outcomes following experimental stroke. This is not too surprising given that several of the neurological dysfunction that occurs in TBI and stroke are similar to those in other neurodegenerative disorders – rooted at the mitochondria – that respond to the neuroprotective effects of ketosis.
Psychiatric Disorders
- There is quite a bit of emerging evidence suggesting that exogenous ketones may help patients with mental disorders, such as anxiety, depression, bipolar, schizophrenia, etc. Research shows that these disorders are associated with changes in brain energy metabolism that alter the similar pathways mentioned above for other brain ailments, including imbalances in neurotransmitters, increased inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired brain glucose metabolism, etc. A review article recently summarized the available research to support the use of exogenous ketones in psychiatric diseases. Based on several lines of evidence, we found that inducing ketosis through supplements should be considered a potential therapeutic strategy in future research due to the overlap of underlying features of these disorders and the metabolic changes and improvements associated with ketosis. Together, it is possible that exogenous ketones may provide benefits to those with psychiatric disorders.
Anxiety
- Several secondary findings in patient populations using ketogenic diets, in addition to animal studies using exogenous ketones, have confirmed behavioral improvements and anti-anxiety effects associated with nutritional ketosis. These effects are thought to be induced by the ketone body, BHB itself and through various mechanisms. One such mechanism may be through changes in the activity of different neurotransmitter systems ultimately leading to increased levels of GABA and adenosine, both of which have been shown to have anti-anxiety effects.
Glucose Metabolism Disorders
There are a number of rare genetic disorders that impair the ability to metabolize carbohydrates, including glucose transporter-1 deficiency syndrome (GLUT-1 DS), glycogen storage disease, pyruvate metabolism disorders, among others. In these conditions, ketones function as an alternative energy substrate, bypassing these inherent defaults and represent a promising treatment strategy.
In fact, a ketogenic diet is the standard of care for GLUT-1 DS and pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency, because ketones circumvent the defect in glucose transporters and metabolism, respectively. Due to the requirement of chronic ketosis, most of these conditions would likely benefit most from a ketogenic diet, where exogenous ketones can supplement and enhance the diet rather than serve as an alternative.
Athletic Performance and Recovery
Interest in the development of exogenous ketones arose from their potential to enhance warfighter physical and cognitive performance. More recent studies have looked at their short-term impact on athletic performance, though the effects are unclear. In 2016, Cox et al. found a 2% increase in performance with the ingestion of an exogenous ketone supplement with carbohydrates versus carbohydrates alone. Exogenous ketosis (full glycogen stores) represents a novel state that differs from endogenous ketosis (empty glycogen stores) and may be advantageous to athletes. That said, exogenous ketones can also be used to complement a ketogenic diet to enhance performance for sports where keto-adaptation may be beneficial. It is likely that when it comes to sports performance, exogenous ketones will favor endurance exercise due to the overlap in the metabolism of aerobic conditions and keto-adaptation. Though, there are several reasons why the benefits of exogenous ketones may be most realized for cognitive enhancement and recovery from training, therefore applying to all athletes. Specifically, exogenous ketones have been shown to limit the rise in lactate following exercise, which may reduce symptoms of fatigue and help accelerate recovery. Also, exogenous ketones have a glycogen- and muscle-sparing effect, which may facilitate glycogen and muscle protein synthesis when co-ingested with carbohydrates and protein post-exercise. Lastly, a recent study found that co-ingesting exogenous ketones with carbohydrates blunted the symptoms of over-training in athletes, suggesting that exogenous ketones may enhance an athlete’s tolerability to regular exercise. More research is needed before direct recommendations and optimal protocols can be established for enhancing athletic performance with exogenous ketones.
Metabolic Health and Type-2 Diabetes
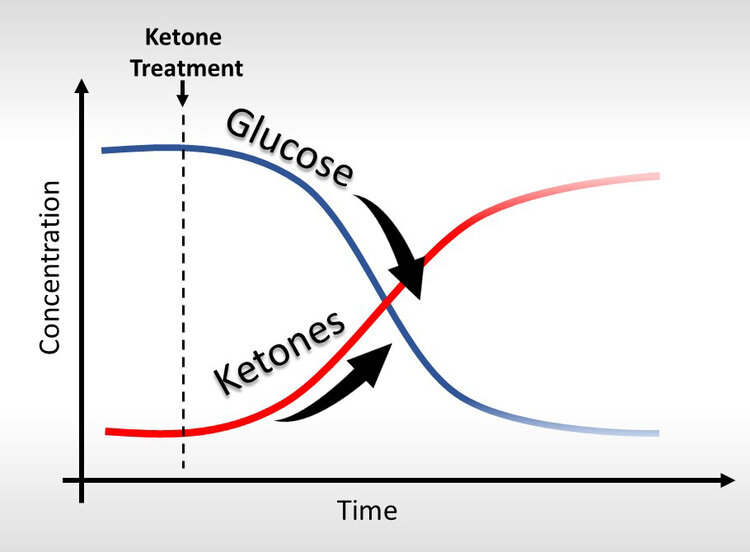
One of the most exciting findings associated with the ingestion of exogenous ketones is the consistent and reliable decrease in blood sugar levels. These findings raise the possibility that exogenous ketones may help those with impaired blood sugar control, such as individuals with insulin resistance and type-2 diabetes. The research is limited in these patient populations, but in healthy, young adults, a ketone ester supplement was shown to reduce blood glucose levels by 16% during an oral glucose tolerance test, compared to control. The exact mechanisms are not understood, but it is thought that consuming exogenous ketones puts the brakes on liver glucose output. The benefits of lowering postprandial blood sugar spikes and controlling blood sugar are unending and apply population-wide. Chronically elevated blood sugar levels can cause damaging effects and contribute to the onset of several chronic diseases. In diabetics, blood sugar control is pertinent for reducing the risk of long-term diabetic complications. Even acutely, managing blood sugar levels has immediate effects on mood, cravings, and appetite. Collectively, by lowering blood glucose, exogenous ketones have the potential to be extremely therapeutic. There is currently a Clinical Trial in their recruiting phase, looking at the effects of exogenous ketone supplements in type-2 diabetes to see if they will improve blood sugar level and improve brain function.
Metabolic Management of Cancer
Due to cancers’ reliance on glucose as its primary fuel for driving the unregulated growth of tumors, ketogenic therapies have become an attractive therapy, replacing glucose with a fuel type that most cancers have difficulty metabolizing, ketones. When using ketogenic therapies in cancer, it is often stressed to achieve a glucose-ketone index (GKI) of 1.0 or below based on preclinical animal models and clinical trials of brain cancer. The glucose-lowering effect of exogenous ketones can help patients achieve a GKI in this therapeutic range by decreasing blood glucose while simultaneously increasing ketones. Experimentally, exogenous ketones have been shown in mice to enhance the anti-cancer effects of ketogenic diets and hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). Lastly, exogenous ketones may protect against cancer-related muscle wasting (cancer cachexia) due to the muscle-sparing and anti-inflammatory effects of ketone bodies. Altogether, ongoing research suggests that exogenous ketones may be a useful complementary cancer therapy.
Wound Healing
Exogenous ketones added to a standard diet of high carbohydrates enhanced wound healing in an ischemic rodent model of wound healing. In other words, wounds healed faster with exogenous ketones. Notably, the ability to heal wounds worsens with age. These studies showed that in aged rats, exogenous ketones increased blood flow leading to greater metabolic activity at the site of the wound and improved healing outcomes, having apparent implications for the elderly. More research is needed to elucidate the exact mechanisms; however, exogenous ketones may represent a potential wound healing therapy.
Initial Adoption of a Ketogenic Diet
A unique application that we think many people can benefit from: when an individual first adopts a ketogenic diet, and thus dramatically restricts carbohydrate intake, they run the risk of experiencing symptoms of what is commonly referred to as the “keto flu” (e.g., headaches, tiredness, irritability, trouble sleeping, among others). These symptoms are often rooted in both the metabolic transition from a predominantly sugar-burner to a fat- and ketone-burner and also electrolyte imbalances due to the natriuresis effect of low insulin levels (which occur when we lower dietary carbohydrates). Exogenous ketone salts can help combat both the low energy state during this metabolic transition, while simultaneously delivering electrolytes to prevent symptoms of electrolyte imbalances.
Bottom Line
Ketosis, as defined by having ketones in the blood, whether induced through fasting, diet, or supplementation, has several therapeutic applications. Although exogenous ketosis is different from endogenous ketosis, their mechanisms often overlap, and emerging peer-reviewed scientific research supports this. Based on the research, the greatest utility of exogenous ketones may be in patient populations who are unwilling or unable to follow a ketogenic diet, to complement a ketogenic diet, or for their potential physical and cognitive enhancements, independent of diet. Future research will help further understand their benefits and establish the most appropriate protocols for both practical and medical applications. If you’re new to exogenous ketones, check out our article on how to choose an exogenous ketone supplement.
Written by: Kristi Storoschuk; Edited by: Dr. Csilla Ari D`Agostino


 Source: Ari et al., 2019
Source: Ari et al., 2019